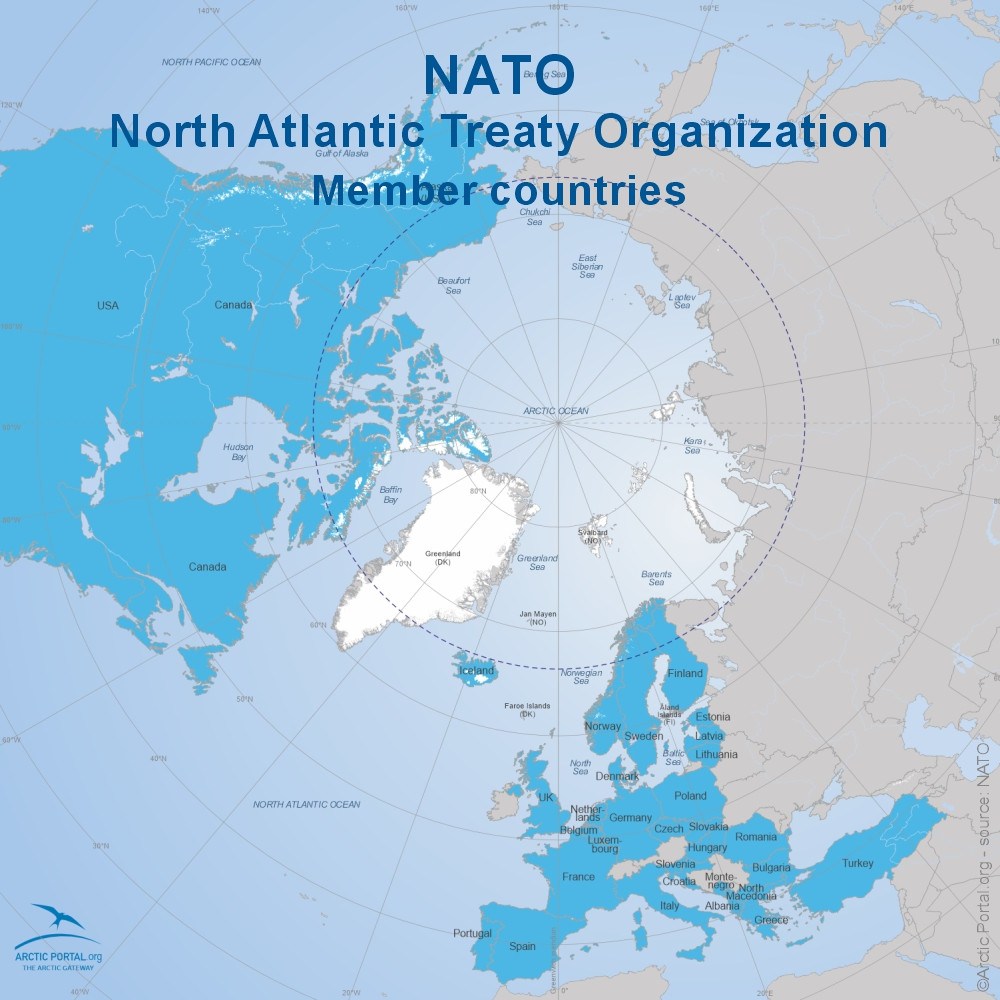
NATO was created by 12 countries from Europe and North America on 4th April 1949.
Since then, 20 more countries have joined NATO through nine rounds of enlargement in:
- 1952 - Greece and Turkey
- 1955 - Germany
- 1982 - Spain
- 1999 - Czechia, Hungary and Poland
- 2004 - Bulgaria, Estonia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia
- 2009 - Albania and Croatia
- 2017 - Montenegro
- 2020 - North Macedonia
- 2023 - Finland
- 2024 - Sweden
At present, NATO has 32 member countries. These countries, called NATO Allies, are sovereign states that come together through NATO to discuss political and security issues and make collective decisions by consensus.
Article 10 of NATO sets out how countries can join the Alliance. It states that membership is open to any
"European State in a position to further the principles of this Treaty and to contribute to the security of the North Atlantic area".
Any decision to invite a country to join the Alliance is taken by the North Atlantic Council, NATO's principal political decision-making body, on the basis of consensus among all Allies.
A Political and Military Alliance
Political
NATO promotes democratic values and enables members to consult and cooperate on defence and security-related issues to solve problems, build trust and, in the long run, prevent conflict.
Military
NATO is committed to the peaceful resolution of disputes. If diplomatic efforts fail, it has the military power to undertake crisis-management operations. These are carried out under the collective defence clause of NATO's founding treaty - Article 5 of the Washington Treaty or under a United Nations mandate, alone or in cooperation with other countries and international organisations.
See also our map of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
Visit our Map Gallery Arctic Portal specializes in creating customized graphical maps that cover a range of significant Arctic topics with global recognition. We are continuously working on new maps and adding them to our Gallery.